Documents generally contain translatable text mixed in with formatting and display information. Because translators are usually only interested in the linguistic content, it is important to separate the translatable text from all of the non-translatable text, such as HTML tags or formatting information.
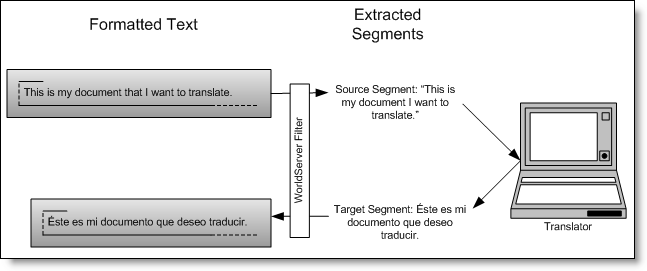
For translation purposes, the WorldServer filtering process starts with a document in one of many formats and breaks it into small, logical units of text called segments. These segments can then be translated and recomposed into a translated target document based on the original source document. The filtering process is mainly performed by file types, which are common both to WorldServer and to SDL Trados Studio.
- Separates formatting from content segments in source documents, based on the document's specific file type. (Sometimes called
decomposing the document.)
For example, in an HTML file, many tags are considered to be non-translatable text while the text between the tags is usually meant for translation.
- Presents the source text segments to translators, so that they can translate the text into the target language.
The translator starts with the segments in a source language (for example, English) and translates those segments into a target language (for example, Japanese).
- Creates (or updates) a target segment with the translated text.
- Recomposes a translated target document based on the original source document and the translated segments.
This process retains the formatting of the original document while replacing the source text with the translated text.
The filtering process automatically creates a target file from the source file. If the target file already exists in the asset interface system, it is updated each time the source file goes through the process. Every time the source document is updated within WorldServer or its timestamp is changed, it is re-segmented according to the rules specified in the file type.
You can configure some aspects of these file types to specify the text to be translated in your documents. The document is then split into segments based on the specific configuration for that specific document file format. For example, a PowerPoint presentation may contain a master file that the client may or may not want translated.
In some cases, WorldServer provides more than one file type for the same file format. Which one you use may depend on your file contents, system platforms, or translation environment. In WorldServer 11.3, you can also configure and use multiple file types for each file format, create new file type configurations or import existing ones from SDL Trados Studio.